Martiniquais Geography, Martinique Geography
Advertisement
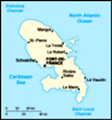
Location: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
Geographic coordinates: 14 40 N, 61 00 W
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area: Total: 1,100 sq km land: 1,060 sq km water: 40 sq km
Area - comparative: Slightly more than six times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 350 km
Maritime claims: Territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: Tropical; moderated by trade winds; rainy season (June to October); vulnerable to devastating cyclones (hurricanes) every eight years on average; average temperature 17.3 degrees C; humid
Terrain: Mountainous with indented coastline; dormant volcano
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m highest point: Montagne Pelee 1,397 m
Natural resources: Coastal scenery and beaches, cultivable land
Land use: Arable land: 10.38% permanent crops: 9.43% other: 80.19% (2001)
Irrigated land: 30 sq km (1998 est.)
Natural hazards: Hurricanes, flooding, and volcanic activity (an average of one major natural disaster every five years)
Environment - current issues: NA
Environment - international agreements:
Geography - note: The island is dominated by Mount Pelee, which on 8 May 1902 erupted and completely destroyed the city of Saint Pierre, killing 30,000 inhabitants
Advertisement
The information here has been derived from Public Domain Sources such as the CIA World Factbook. No liability can be taken for any inaccuracies.
Tot: 0.033s; Tpl: 0.007s; cc: 5; qc: 8; dbt: 0.0091s; 1; m:domysql w:travelblog (10.17.0.13); sld: 1;
; mem: 1.1mb
 Colonized by France in 1635, the island has subsequently remained a French possession except for three brief periods of foreign occupation....
Colonized by France in 1635, the island has subsequently remained a French possession except for three brief periods of foreign occupation....